Биология - Дезаминирование
09 февраля 2011процесс удаления аминогрупп от молекулы. Ферменты, катализирующие дезаминирование, называют деаминазами.
В организме человека дезаминирование в основном происходит в печени, однако, глютамат дезаминируется также и в почках. Аминогруппа, которая удаляется от аминокислот в ходе дезаминирования, превращается далее в аммиак. Остов аминокислоты, состоящий из атомов углерода и водорода, может далее использоваться в реакциях анаболизма или катаболизма. Аммиак является токсичным для человека, поэтому существуют ферменты, превращающие аммиак в мочевину или мочевую кислоту.
Дезаминирование в ДНК
Цитозин
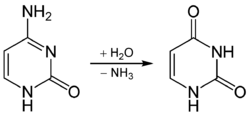
Spontaneous deamination is the hydrolysis reaction of cytosine into uracil, releasing ammonia in the process. This can occur in vitro through the use of bisulfite, which converts cytosine, but not 5-methylcytosine. This property has allowed researchers to sequence methylated DNA to distinguish non-methylated cytosine and methylated cytosine.
In DNA, this spontaneous deamination is corrected for by the removal of uracil by uracil-DNA glycosylase, generating an abasic site. The resulting abasic site is then recognised by enzymes that break a phosphodiester bond in the DNA, permitting the repair of the resulting lesion by replacement with another cytosine. A Family A DNA Polymerase may perform this replacement via nick translation, a terminal excision reaction by its 3'-->5' exonuclease activity, followed by a fill-in reaction by its polymerase activity. DNA ligase then forms a phosphodiester bond to seal the resulting nicked duplex product, which now includes a new, correct cytosine.
5-метилцитозин
Spontaneous deamination of 5-methylcytosine results in thymine and ammonia. This is the most common single nucleotide mutation. In DNA, this reaction cannot be corrected because the repair mechanisms do not recognize thymine as erroneous, and, unless it affects the function of the gene, the mutation will persist. This flaw in the repair mechanism contributes to the rarity of CpG sites in the eukaryotic genome.
Гуанин
Deamination of guanine results in the formation of xanthine. Xanthine, in a manner analogous to the enol tautomer of guanine, selectively base pairs with thymine instead of cytosine. This results in a post-replicative transition mutation, where the original G-C base pair transforms into an A-T base pair. Correction of this mutation involves the use of alkyladenine glycosylase during base excision repair.
Аденин
В результате дезаминирования аденина образуется гипоксантин, который имеет структуру, сходную с таутомером аденина, и спаривается с цитозином вместо тимина. Происходит транзиция A-T в G-C.
Просмотров: 9167
|
|
